Heterogeneous nucleation definition 156850-Homogeneous nucleation rate
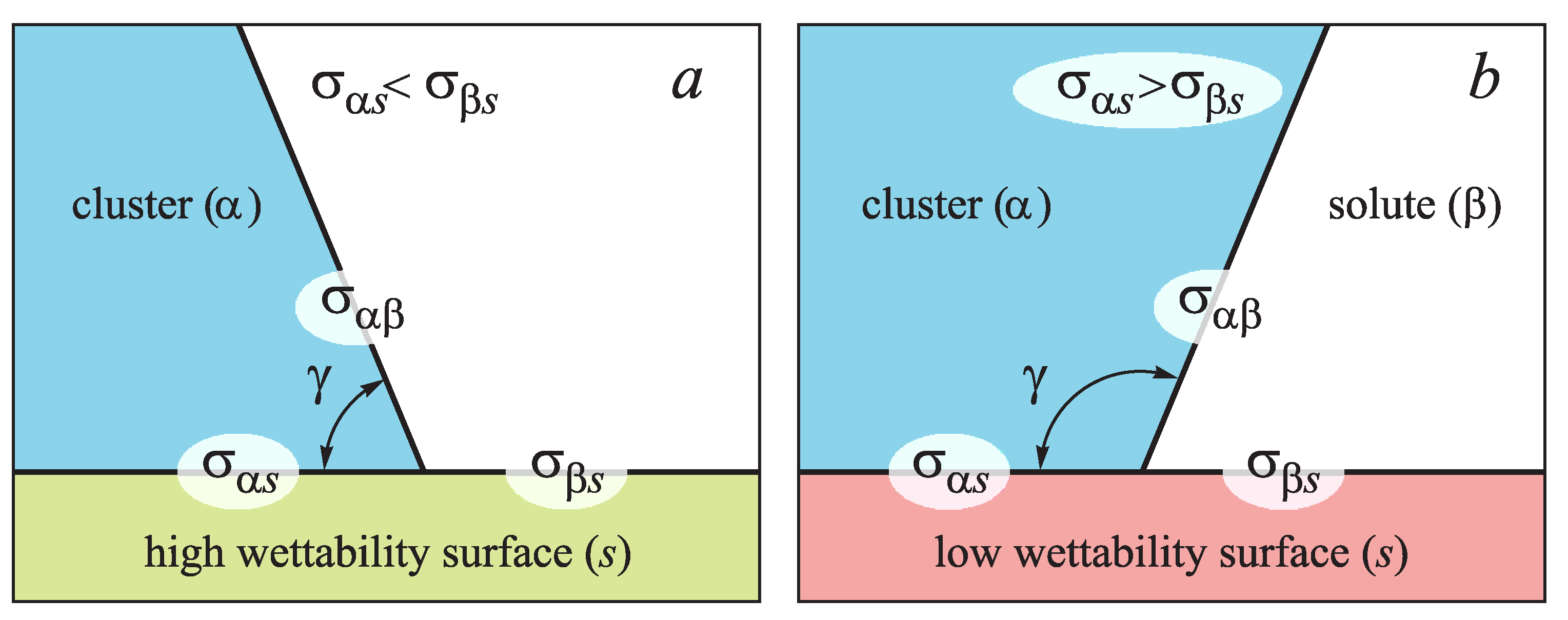
This is called heterogeneous nucleation, which requires less activation energy than homogeneous nucleation Foreign particles can apply part of the activation energy, so that even smaller nuclei can grow!Freezing nucleation can be divided into homogeneous nucleation and heterogeneous nucleation Study on the Phase Change Characteristics of CarbonBased Nanofluids These findings ie predominance of sulphate emissions at maximum load modes further ratifies the argument that, it is actually heterogeneous nucleation which increases both nuclei mode NP as well as sulphate212 Heterogeneous nucleation In the usual casting processes, nucleation is heterogeneous and occurs on solid surfaces in the liquid Foreign substances, either the container or insoluble impurities, provide such surfaces For a metal to solidify on a foreign substance, it is essential that the surface of the substrate should be wetted The angle of contact θ between the substrate and

What Is Nucleation What Does Nucleation Mean Nucleation Meaning Definition Explanation Youtube
Homogeneous nucleation rate
Homogeneous nucleation rate-Nucleation meaning and definition Noun nucleationThe process of forming a click for more detailed meaning in English, definition, pronunciation and example sentences for nucleationHeterogeneous nucleation occurs much more often than homogeneous nucleation It forms at preferential sites such as phase boundaries or impurities like dust and requires less energy than homogeneous nucleation At such preferential sites, the effective surface energy is lower, thus diminishing the free energy barrier and facilitating nucleation Surfaces promote nucleation




The Theory Of Ice Nucleation By Heterogeneous Freezing Of Deliquescent Mixed Ccn Part I Critical Radius Energy And Nucleation Rate In Journal Of The Atmospheric Sciences Volume 61 Issue 22 04
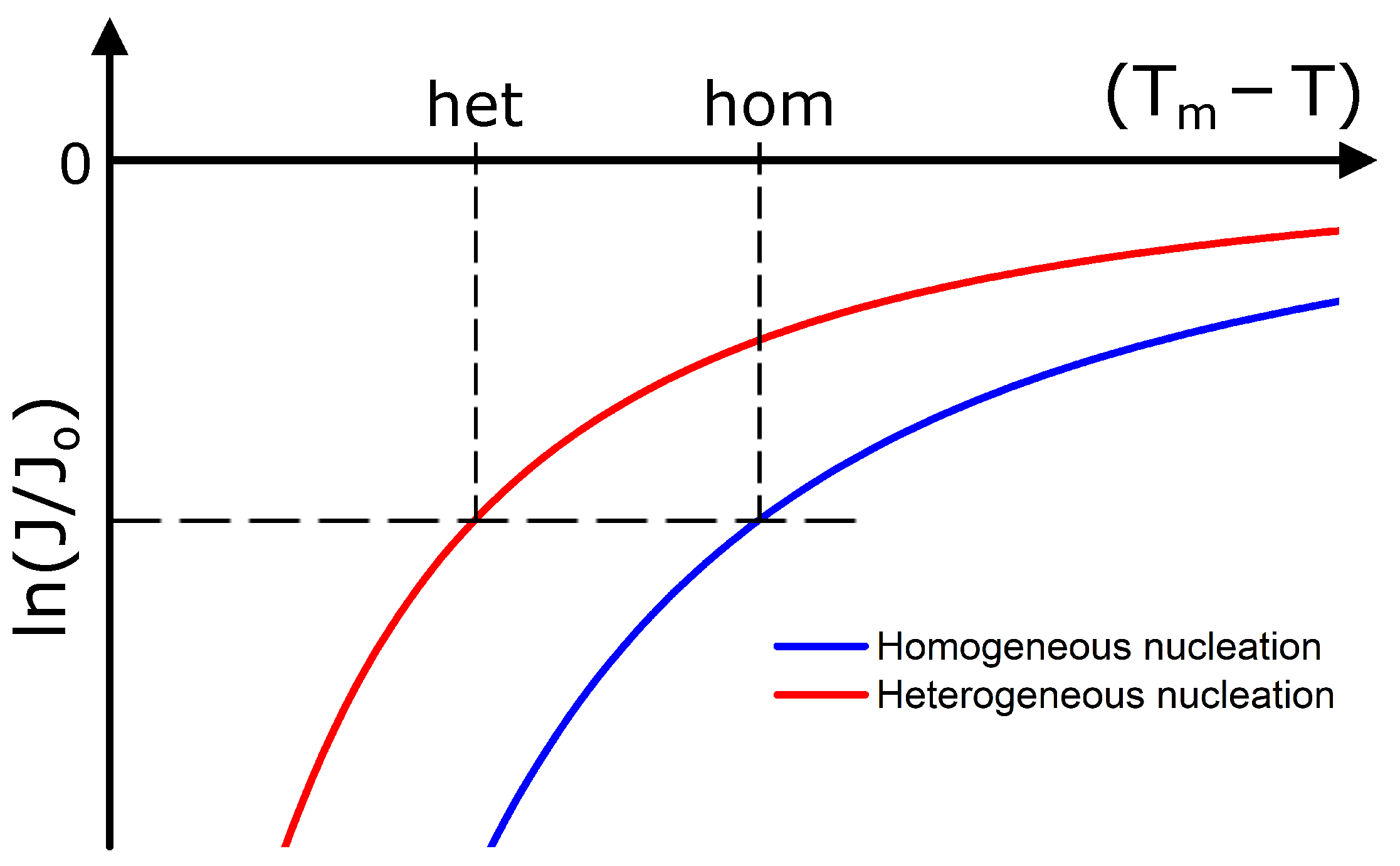
On flat walls, heterogeneous nucleation will typically overwhelm homogeneous nucleation Even for surfaces randomly coated with spheres with a diameter that was some three times larger than that of the fluid spheres – as has been used in some experiments – heterogeneous nucleation is likely to be dominant for volume fractions smaller than ∼0535 Only for a disordered coating that has the same structure as the liquid did we find that nucleationHeterogeneous nucleation applies to the phase transformation between any two phases of gas, liquid, or solid, typically for example, condensation of gas/vapor, solidification from liquid, bubble formation from liquid, etcIn the latter, a few particles come into correct juxtaposition in the course of their random movement through the bulk of the medium
In general, heterogeneous nucleation occurs more easily than homogenous nucleation and allows the freezing process to occur at higher temperatures and with a shorter phase change timePrimary nucleation agenda 1 Definitions, applications and solubility plot 2 Thermodynamics 3 Kinetics 4 How to measure primary nucleation rate 5 Heterogeneous nucleation 6 Polymorphs nucleation 7 Nonclassical nucleation pathway 8 References 2 Separation Processes Laboratory Prof Mazzotti Rate Controlled Separations Definition of nucleation 3 "The importance of nucleationInformation and translations of nucléation in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web
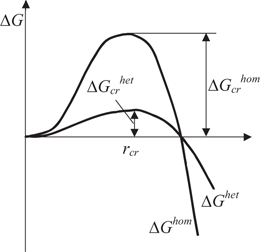
Lecture 14 Rate of Nucleation Today's topics • Two energetic factors that affect nucleation rate the activation energy barrier (∆G*) that needs to be overcome to produce a criticalsize nucleus, and the activation energy for an atom to migrate across the interface separating the nucleus and matrix, and thus get attached to the growing incipient nucleus • Temperature dependence ofEn pratique la nucléation est très généralement hétérogène dans l' air et dans les solutions aqueuses en raison de l'abondance des particules solides ou fluides d'autres phases (poussières, gouttelettes, bulles), sauf quand ils sont particulièrement purs Elle est en revanche souvent homogène dans les sels fondusHeterogeneous nucleation is the case when the crystallization is aided by the presence of impurities The impurities that aid crystallization are termed as catalyzers In case of heterogeneous nucleation, there are three interfaces to be considered the liquid catalyzer interface, the solid catalyzer interface, and the solid liquid interface
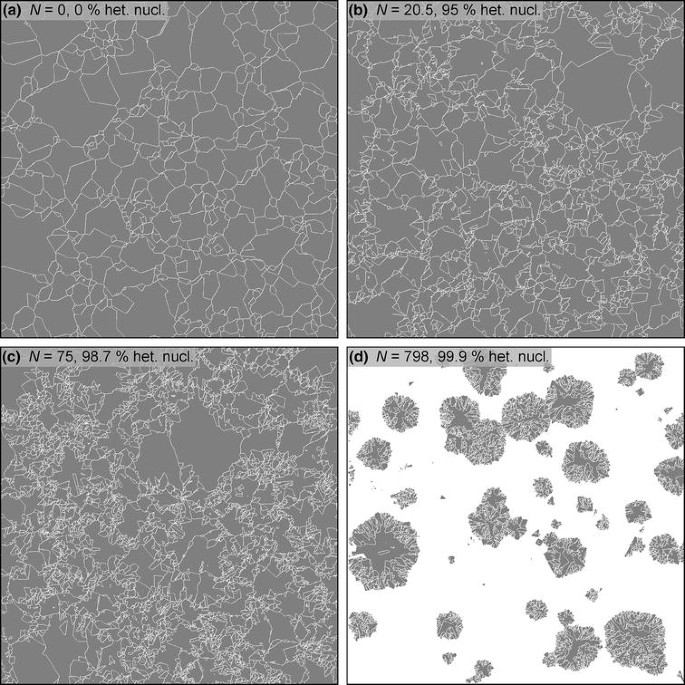



Heterogeneous Nucleation As The Predominant Mode Of Crystallization In Natural Magmas Numerical Model And Implications For Crystal Melt Interaction Springerlink
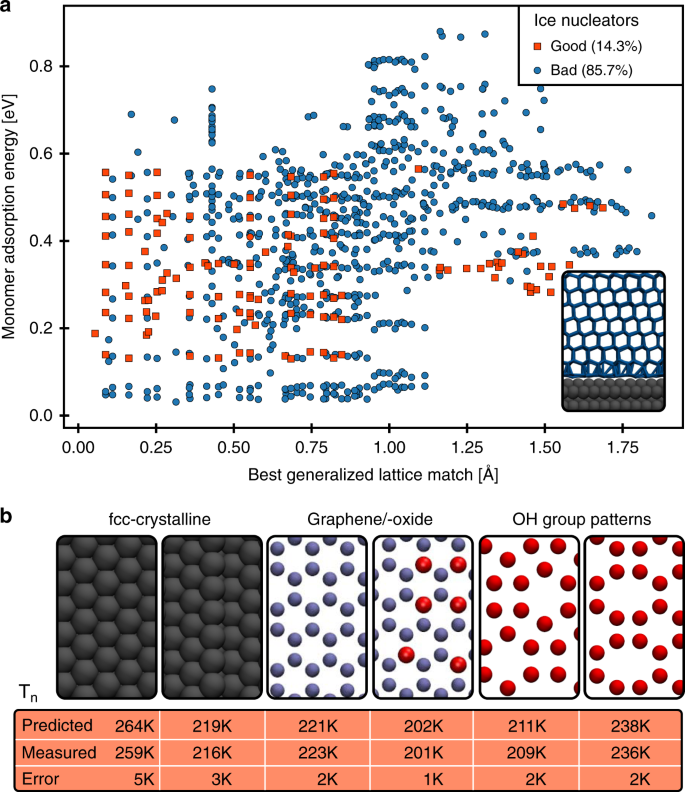



Predicting Heterogeneous Ice Nucleation With A Data Driven Approach Nature Communications
As a result, distinguishing between heterogeneous and homogeneous nucleation is frequently essential Heterogeneous nucleation takes place at nucleation sites on the system's surfaces Away from a surface, homogeneous nucleation occurs As already studied nucleation definition, let's discuss nucleation and growth in detail To Calculate Nucleation Rate If the system is not Heterogeneous nucleation occurs when nuclei begin to form on some sort of impurity and grow outward from the impurity An example is a molten metal solidifying on the walls of a crucible Some of the metal nucleation will occur on the crucible wall and grow outward from there In particular, we reveal three new transition pathways ingrain homogeneous nucleation driven by spontaneous dislocation generation, heterogeneous nucleation assisted by premelting grain




2 12 Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Nucleation Kinetics Of Structural Transformations Coursera




Heterogeneous Nucleation Youtube
What does NUCLEATION mean?Heterogeneous nucleation begins on alien surfaces or particles, or preexisting nuclei in the old phase Dust or atmospheric aerosols can serve as heterogeneous nucleation centers for water condensation in the atmosphere Likewise, the microscopically rough surface of a Champagne glass offers nucleation sites for CO 2 bubbles (see picture above)Nucleation Definition nucleation may be defined as the first irreversible formation of a nucleus of the new (equilibrium) phase Nucleation Prerequisite to bring the system temporary into a thermodynamic unstable state crossing phase boundaries a nucleus or a cluster is a small ensemble of molecules / atoms of the new phase Some Remarks (Key Points) one molecule cannot form a



Lecture 25
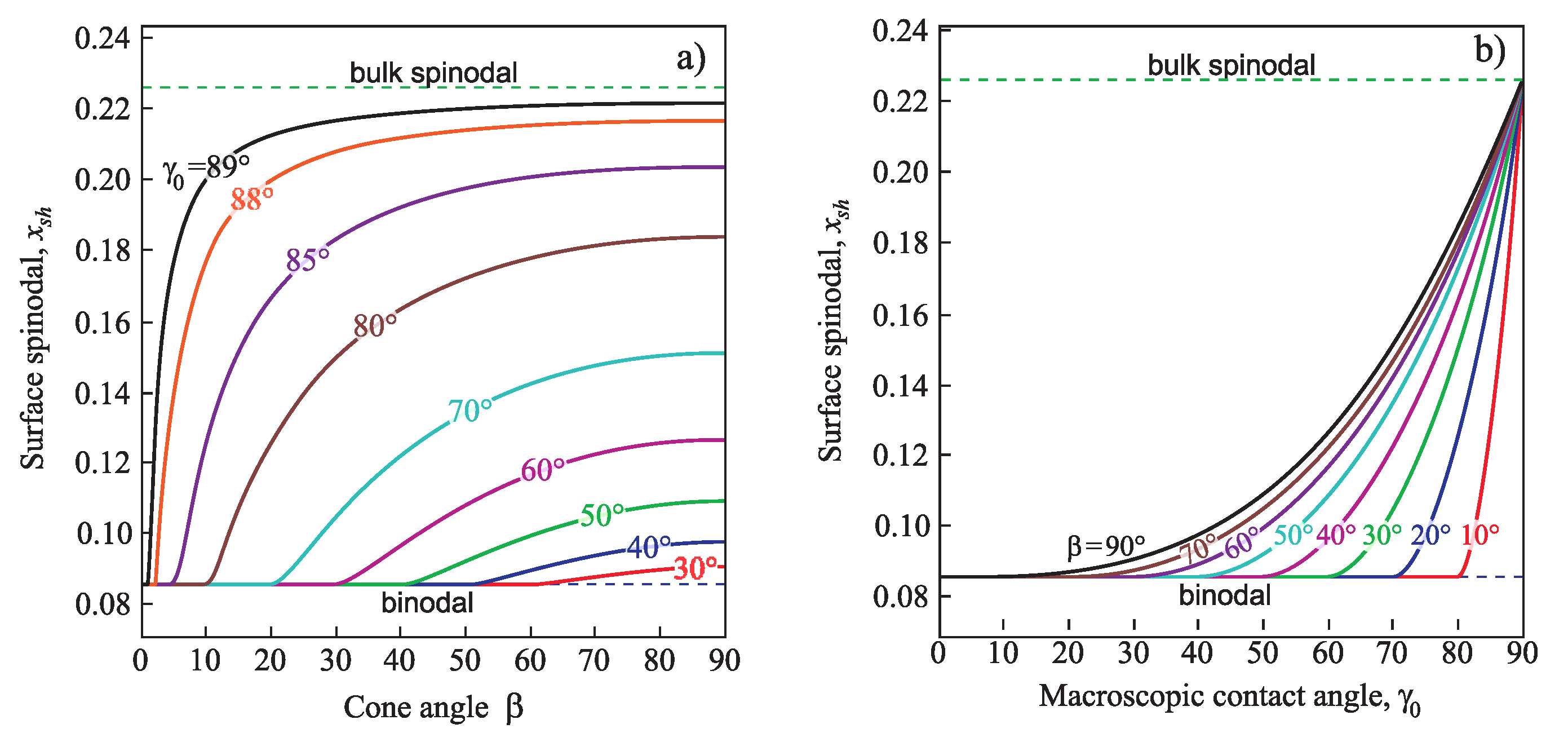



Entropy Free Full Text Heterogeneous Nucleation In Solutions On Rough Solid Surfaces Generalized Gibbs Approach Html
Read 9 answers by scientists to the question asked by Hang Zhai on Our working definition of the socalled supercooling point , often approximated in biological studies, is the temperature at which, on average, 50% of the samples are frozen Elsewhere we show this corresponds quite accurately to the maximum of the derivative of the survival curve, sometimes called the nucleation rate The full width at half height of that A heterogeneous mixture is a mixture in which the components of the mixture are not uniform or have localized regions with different properties Different samples from the mixture are not identical to each other There are always two or more phases in a heterogeneous mixture, where you can identify a region with properties that are distinct from those of another region,



Introduction To Nucleation




Chapter 1 Cavitation And Bubble Dynamics Christopher E Brennen
Since a melt usually always contains such foreign particles, heterogeneous nucleation is therefore much more likely than homogeneous nucleationHomogenous * Homogenous the nucleation takes place in a liquid metal without the help of any impurities * Occurs in perfectly homogenous materials such as pure liquid * When pure liquid metal is colled below its equilibrium, freezing temperaturNucleation processes are classed as heterogeneous or homogeneous In the former, the surface of some different substance, such as a dust particle or the wall of the container, acts as the centre upon which the first atoms, ions, or molecules of the crystal become properly oriented;




Nucleation Of Melt From Fundamentals To Dispersed Systems Sciencedirect




Chapter 1 Cavitation And Bubble Dynamics Christopher E Brennen
Heterogeneous nucleation is the most effective mechanism for the inception of phase transformation Solid walls and impurities act as a catalyst for the formation of a new thermodynamic phase by reducing the activation energy required for a phase change, hence enhancing nucleation The formation of vapour bubbles close to solid, ideally flat, walls is642 Heterogeneous Nucleation Homogeneous nucleation occurs only rarely It is virtually always the case that nucleation processes are catalyzed by a heterogeneity such as an accommodating substrate surface The liquid cap wetting a flat substrate in Fig 533 may be viewed as an example of heterogeneous nucleation Because of the bonding across the substrate interface, less energyFind out what is the full meaning of HETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION on Abbreviationscom!




Difference Between Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Nucleation Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms



Introduction To Nucleation
Heterogeneous nucleation, nucleation with the nucleus at a surface, is much more common than homogeneous nucleation springer The mechanism of heterogeneous nucleation and the relation between nucleation density and undercooling are discussedHETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION ON A SUBSTRATE 551 this maximum energy barrier of formation, and it is finally this difficulty that limits the rate of formation of a new stable phase The cluster of size x = x* is called the critical cluster or often the critical nucleus Heterogeneous nucleation, which occurs when ice begins to form around a nucleation site, such as a physical disturbance, an impurity (such as salt) in the liquid or an irregularity in a container Since biological samples are never pure water, they always experience heterogeneous nucleation Homogenous nucleation, which occurs when ice forms without any predefined nucleation




Classical Nucleation Theory Wikiwand




Nucleation Intechopen
Tu peux également retrouver des opinions sur nucleation heterogeneous et découvrir ce que les autres pensent de nucleation heterogeneous Tu peux donc donner ton opinion sur ce thème, mais aussi sur d'autres sujets associés à nucleation, heterogeneous, nucléation définition, nucléation croissance, agents de nucléation et quest ce que la nucléationMost nucleation processes are physical, rather than chemical Nucleation normally occurs at nucleation sites on surfaces contacting the liquid or vapor Suspended particles or minute bubbles also provide nucleation sites This is called heterogeneous nucleation (Lecture 12) To be able to control the functions of engineered multicomponent nanomaterials, a detailed understanding of heterogeneous nucleation at the nanoscale is essential Here, by using in
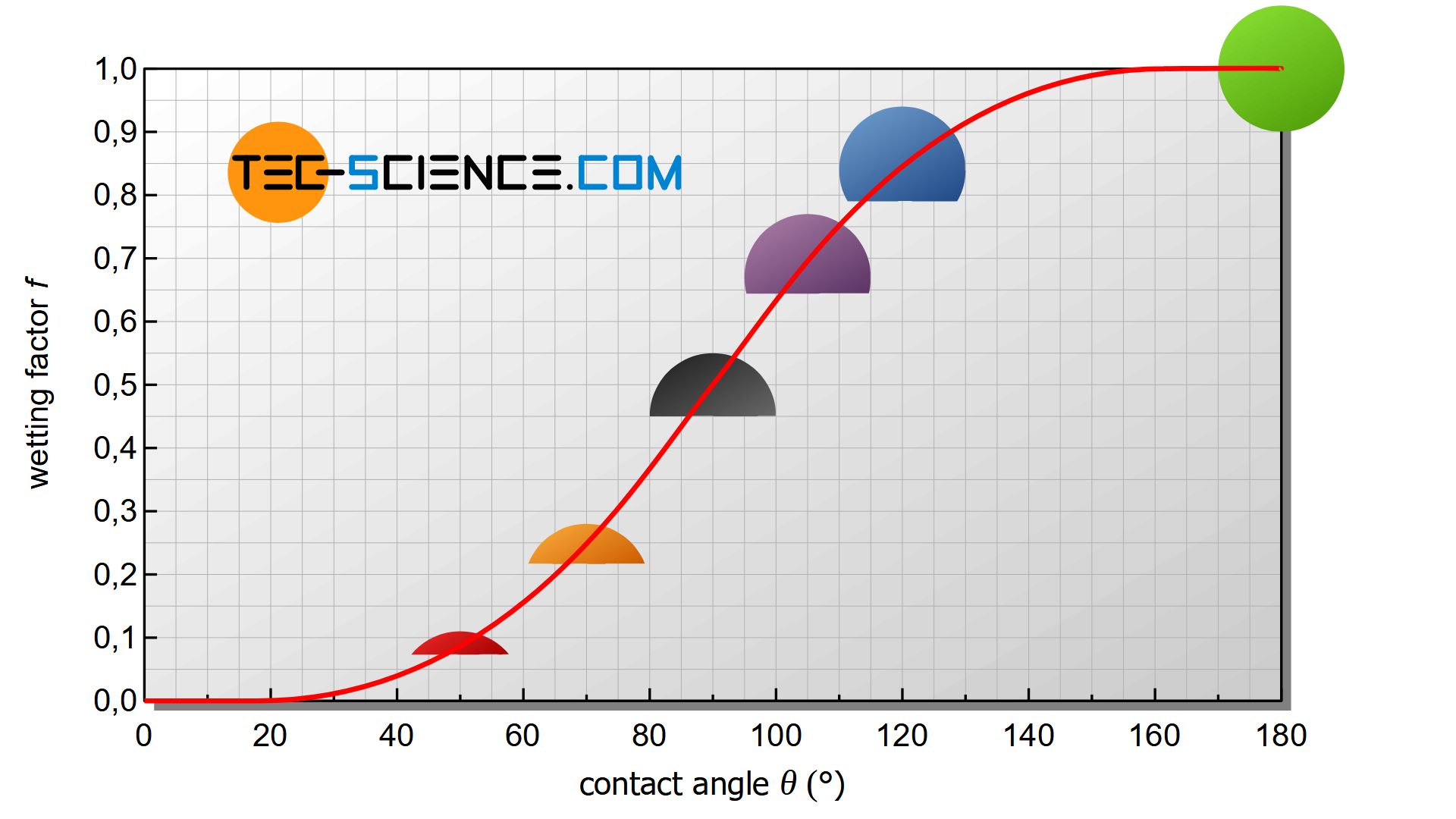



Heterogeneous Nucleation Tec Science




Ema5001 L13 03 Heterogeneous Nucleation Rate For Solidification Youtube
There are natural homogeneous nucleation sites in the metal and others (heterogeneous nucleation sites) that are the result of inoculationDefinition of nucléation in the Definitionsnet dictionary Meaning of nucléation What does nucléation mean?Heterogeneous nucleation Nuclear processes, like a suitable substrate surface, are nearly always catalyzed by heterogeneity The connection across the substratum interface uses less energy to




Heterogeneous Nucleation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Http Catalan Quim Ucm Es Pdf Hs Heterogeneous Published Pdf
Homogeneous nucleation nucleation about a nidus composed of material identical with that precipitatingHomogeneous and heterogeneous nucleationLe différence clé entre nucléation homogène et hétérogène est que le la nucléation homogène se produit loin de la surface du système tandis que la nucléation hétérogène se produit à la surface du système La nucléation est l'étape initiale du processus de formation d'une nouvelle phase thermodynamique ou d'une nouvelle structure via l'autoorganisation




Quantitative Evaluation On The Heterogeneous Nucleation Of Amino Acid By A Thermodynamic Analysis Sciencedirect




Solidification Of Material
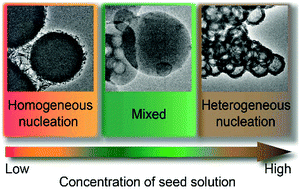
Heterogeneous nucleation, nucleation with the nucleus at a surface, is much more common than homogeneous nucleation For example, in the nucleation of ice from supercooled water droplets, purifying the water to remove all or almost all impurities results in water droplets that freeze below around −35 °C, whereas water that contains impurities may freeze at −5 °C or warmerNucleation sites), low viscosity, and low critical energy barrier are favoring the formation of a large number of nuclei For a given concentration of solute, a larger number of nuclei mean smaller sized nuclei Figure 34 schematically illustrated the processes of nucleation and subsequent growth When the concentration of solute increases as a function of time, no nucleation would occur Nucleation is affected by the level of impurities in a system, which can provide surfaces to support assembly In heterogeneous nucleation, organization begins at nucleation points on surfaces In homogeneous nucleation, organization occurs away from a surface For example, sugar crystals growing on a string is an example of heterogeneous nucleation Another



Pubs Acs Org Doi Pdf 10 1021 Acs Chemrev 5b



Nucleation Soft Matter
Define nucleation nucleation synonyms, nucleation pronunciation, nucleation translation, English dictionary definition of nucleation adj Nucleated v nu·cle·at·ed , nu·cle·at·ing , nu·cle·ates v tr 1 To bring together into a nucleus 2 To act as a nucleus for 3 To provide aNUCLEATION meaning NUCLEATION pronunciation NUCLEATION definition NUCLEATION meaning NUCLEATION pronunciation NUCLEATION definitionDefinition from Wiktionary, the free dictionary Jump to navigation Jump to search English Etymology hetero nucleationNoun heteronucleation (plural heteronucleations) heterogeneous nucleation (for example, caused by particles of impurities)



Heterogeneous Nucleation And Growth Of Highly Crystalline Imine Linked Covalent Organic Frameworks Chemical Communications Rsc Publishing




Bubble Nucleation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
In heterogeneous Nucleation, organization begins at Nucleation points on surfaces 4 Nucleation is a random process which in two same situations or system Nucleation will happen at a different time 4, 7 5 Generally, the theory introduces in describing this phenomenon include its nature and behavior of the new thermodynamic phase is called classical Nucleation theoryNucleation characteristics Nucleation is a process that usually occurs with more difficulty inside a uniform substanceIt is characterized because the thermal activation that it possesses will provide the necessary energy to be able to give form to a stable nucleusIt has two different types, homogeneous and heterogeneousThis process can be called as a new phase developmentFor homogeneous nucleation the surface area is simply that of a sphere For heterogeneous nucleation, however, the surface area is smaller since part of the nucleus boundary is accommodated by the surface or impurity onto which it is nucleating There are several factors which determine the precise reduction in the exposed surface area




Chap 9 Surface Thermodynamics And Nucleation Of Water



Q Tbn And9gcsygt2rt015bhsgmvdznkfw Ram7jza2holfb3zxcn9huitxwjo Usqp Cau
Heterogeneous nucleation is the process of nucleation that takes place at the surface of the system (in which the nucleation occurs) It is faster than the homogeneous type nucleation Further, this type of nucleation occurs at nucleation sites;Looking for the definition of HETEROGENEOUS NUCLEATION?Nucleation processes are classed as heterogeneous or homogeneous In the former, the surface of some different substance, such as a dust particle or the wall of the container, acts as the centre upon which the first atoms, ions, or molecules of the crystal become properly oriented;



Nucleation And Growth Kinetics Nanoscale Solidification Springerlink




Nucleation Studies In The Martian Atmosphere Maattanen 05 Journal Of Geophysical Research Planets Wiley Online Library
The Web's largest and most authoritative acronyms and abbreviations resource




Chap 9 Surface Thermodynamics And Nucleation Of Water Droplets And Ice Crystals Ppt Download




15 A Define Heterogeneous Nucleation 3 B Where Chegg Com



Crystals Free Full Text Heterogeneous Crystal Nucleation From The Melt In Polyethylene Oxide Droplets On Graphite Kinetics And Microscopic Structure Html




3 Define The Critical Radius Of Nucleus Of A Chegg Com




Pdf Lecture 2 Homogeneous Nucleation




Inoculants Size In Hetorogenuose Nucleation




Lecture 7 Quick Review We Discussed The Meaning Of The Critical R And G Since It S Unstable If We Can Form A Drop With R R The System Will Ppt Download



Homogeneous Nucleation



Entropy Free Full Text Heterogeneous Nucleation In Solutions On Rough Solid Surfaces Generalized Gibbs Approach Html



Solidification Book Chapter Iopscience




Principles Of Mimicking And Engineering The Self Organized Structure Of Hard Tissues Journal Of Biological Chemistry




Illustration Of Homogeneous Nucleation And Heterogeneous Nucleation Download Scientific Diagram




Plot Of D G Versus R For Homogeneous Nucleation And An Example Of Download Scientific Diagram




Mit Microstructural Evolution In Materials 12 Nucleation Ppt Download
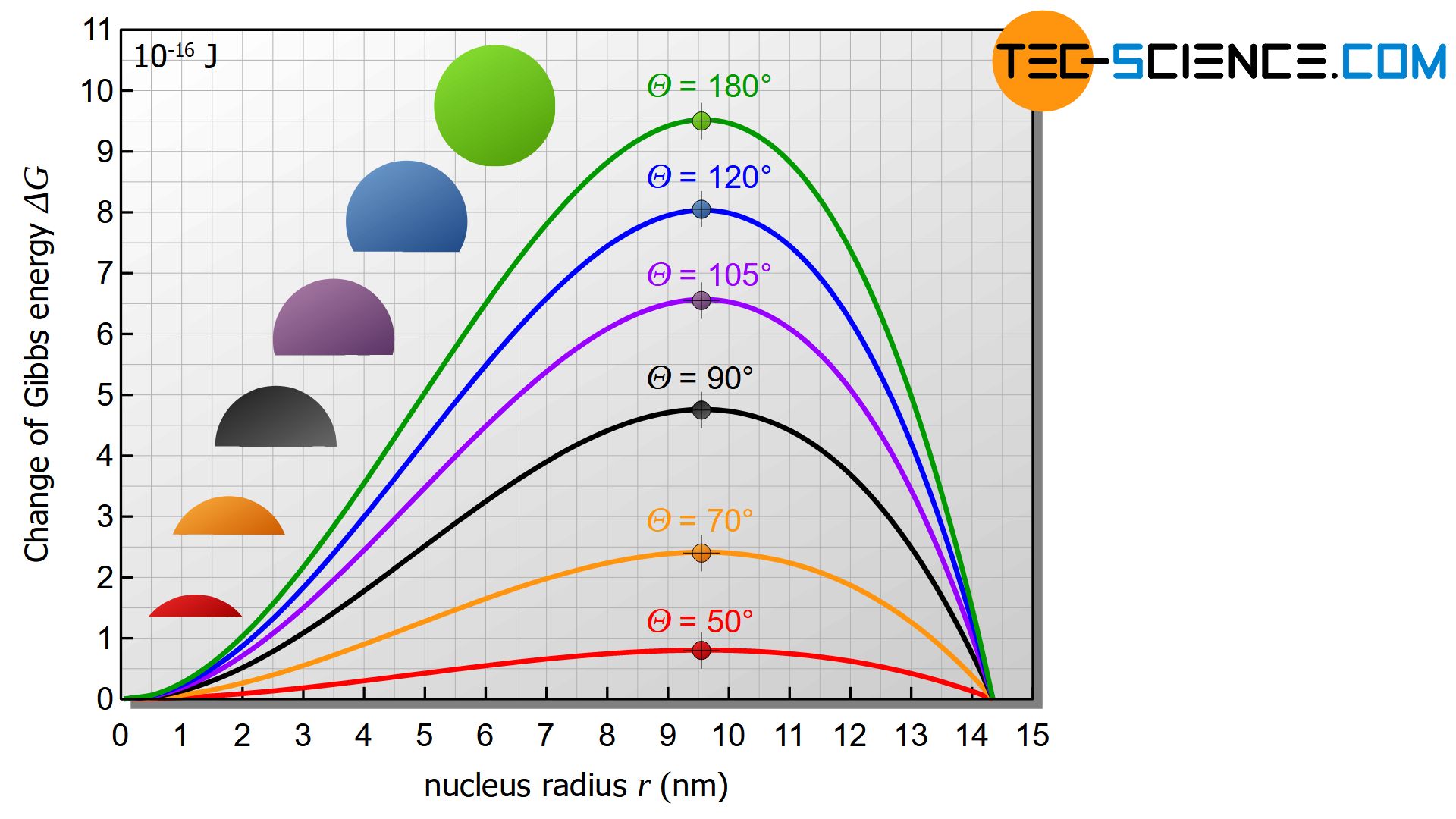



Heterogeneous Nucleation Tec Science




Heterogeneous Nucleation In Sickle Hemoglobin Experimental Validation Of A Structural Mechanism Sciencedirect




Inoculants Size In Hetorogenuose Nucleation




Quantitative Evaluation On The Heterogeneous Nucleation Of Amino Acid By A Thermodynamic Analysis Sciencedirect
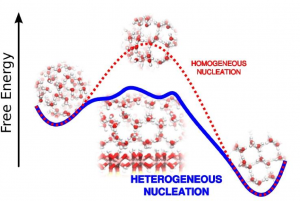



Ice Nucleation The Ice Group




Homogeneous Nucleation Youtube




15 A Define Heterogeneous Nucleation 3 The Chegg Com




The Theory Of Ice Nucleation By Heterogeneous Freezing Of Deliquescent Mixed Ccn Part I Critical Radius Energy And Nucleation Rate In Journal Of The Atmospheric Sciences Volume 61 Issue 22 04



The Heterogeneous Nucleation Blog About Quality Control Of Metal




Heterogeneous Nucleation In Solutions Generalized Gibbs Approach The Journal Of Chemical Physics Vol 140 No 24



Http Wiredspace Wits Ac Za Bitstream Handle 1687 02chapter2 Pdf Sequence 5




Lecture 12 Heterogeneous Nucleation A Surface Catalyzed Process Pdf Free Download




Lecture 12 Heterogeneous Nucleation A Surface Catalyzed Process Pdf Free Download




Critical Radius Wikipedia




Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Nucleation Youtube




Nucleation Intechopen




Nucleation Wikipedia



My Eng Utah Edu Lzang Images Lecture 12 Pdf




Heterogeneous Nucleation In Solutions Generalized Gibbs Approach The Journal Of Chemical Physics Vol 140 No 24



Lecture 25




Objectives Template



Gmd A New Parameterization Of Ice Heterogeneous Nucleation Coupled To Aerosol Chemistry In Wrf Chem Model Version 3 5 1 Evaluation Through Isdac Measurements
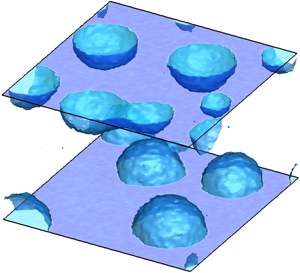



Heterogeneous Bubble Nucleation Dynamics Journal Of Fluid Mechanics Cambridge Core
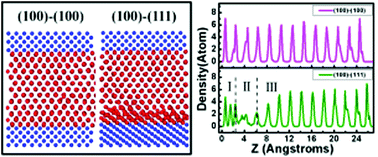



Heterogeneous Nucleation Of Al Melt In Symmetrical Or Asymmetrical Confined Nanoslits Nanoscale Rsc Publishing
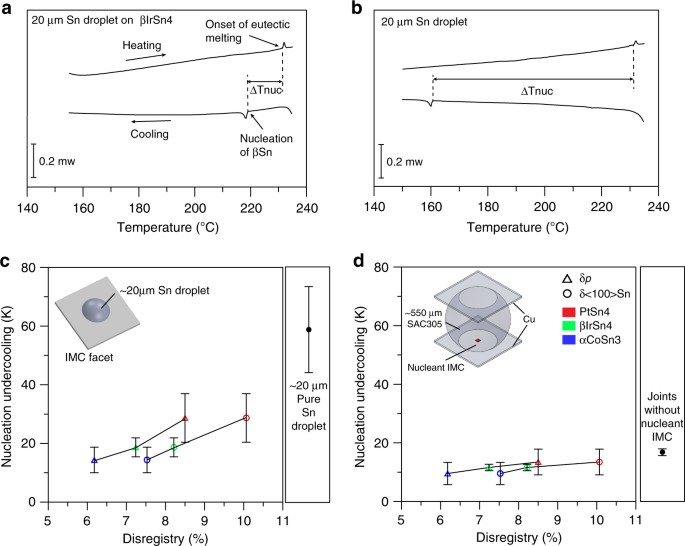



Harnessing Heterogeneous Nucleation To Control Tin Orientations In Electronic Interconnections Nature Communications
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Nucleation_finger-5c0929e446e0fb0001d70a48.jpg)



Nucleation Definition Chemistry And Physics



1




The Theory Of Ice Nucleation By Heterogeneous Freezing Of Deliquescent Mixed Ccn Part I Critical Radius Energy And Nucleation Rate In Journal Of The Atmospheric Sciences Volume 61 Issue 22 04




Crystal Nucleation Chapter 3 Handbook Of Industrial Crystallization




Thermodynamic And Kinetics Investigation Of Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Nucleation




Heterogeneous Nucleation Crystallography Britannica




Homogeneous Nucleation




Heterogeneous Nucleation Toward Polar Solvent Free Fast And One Pot Synthesis Of Highly Uniform Perovskite Quantum Dots For Wider Color Gamut Display Li 18 Advanced Materials Interfaces Wiley Online Library




Inoculants Size In Hetorogenuose Nucleation




The Formation Of A Solid Nucleus As Shown In Figure Chegg Com




Heterogeneous Ice Nucleation In The Tropical Tropopause Layer Jensen 18 Journal Of Geophysical Research Atmospheres Wiley Online Library




A Homogeneous Nucleation B Heterogeneous Nucleation Download Scientific Diagram
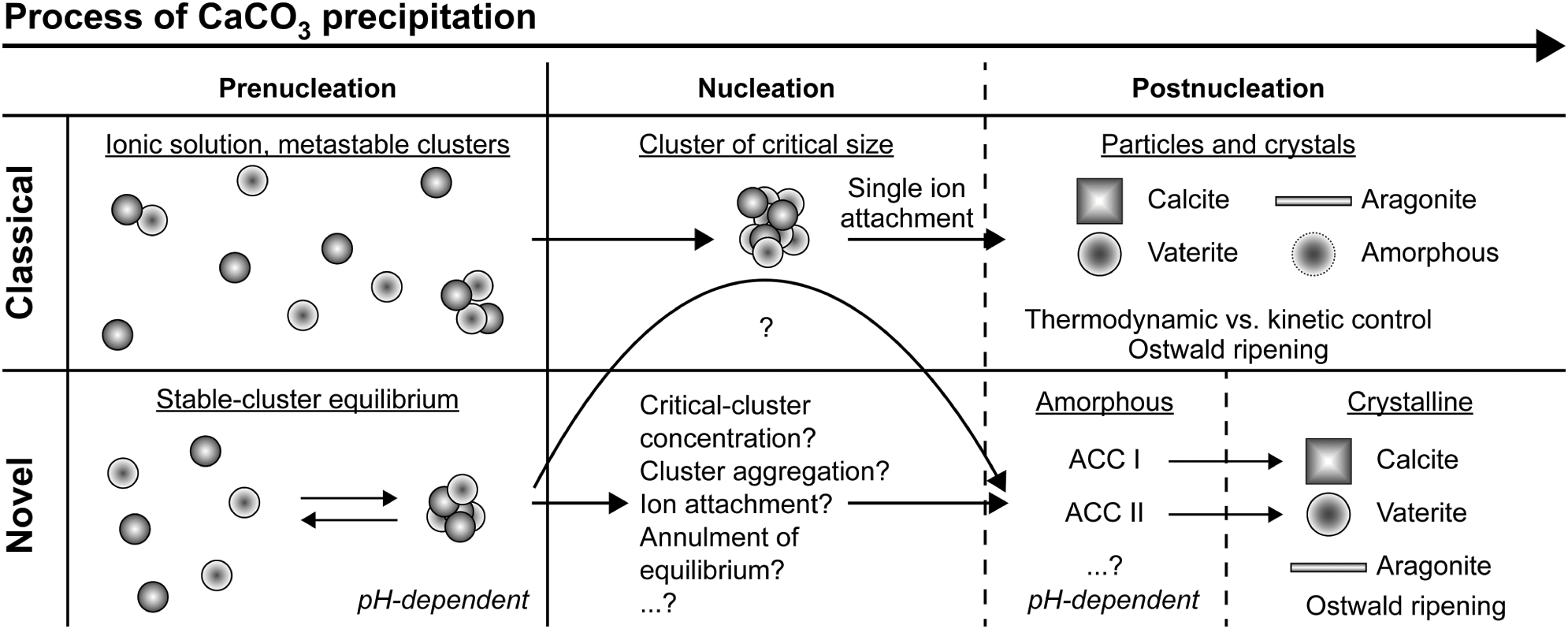



Crystal Nucleation Chapter 3 Handbook Of Industrial Crystallization




Chap 9 Surface Thermodynamics And Nucleation Of Water
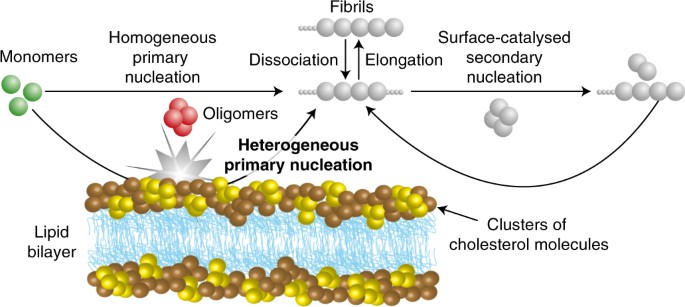



Cholesterol Catalyses Ab42 Aggregation Through A Heterogeneous Nucleation Pathway In The Presence Of Lipid Membranes Nature Chemistry




Heterogeneous Nucleation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



1




Crystal Nucleation Chapter 3 Handbook Of Industrial Crystallization




Thermodynamic And Kinetics Investigation Of Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Nucleation




What Is Nucleation What Does Nucleation Mean Nucleation Meaning Definition Explanation Youtube




Heterogeneous Nucleation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Experiment And Theory For Heterogeneous Nucleation Of Protein Crystals In A Porous Medium Pnas



316 2 Microstructural Dynamics Ii




Supersaturation Nucleation Crystal Growth Crystal Non Equilibrium Equilibrium Ppt Download
/diamond-against-black-background--close-up-607873447-59b69f1203f4020010b53942.jpg)



Nucleation Definition Chemistry And Physics



1




Homogeneous Nucleation




Experiment And Theory For Heterogeneous Nucleation Of Protein Crystals In A Porous Medium Pnas



Http Catalan Quim Ucm Es Pdf Hs Heterogeneous Published Pdf




Nucleation Wikipedia




Heterogeneous Nucleation Of Supercooled Water And The Effect Of An Added Catalyst Pnas




Heterogeneous Nucleation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
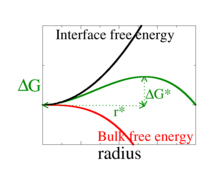



Classical Nucleation Theory Wikipedia




Thermodynamic And Kinetics Investigation Of Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Nucleation




Thermodynamic And Kinetics Investigation Of Homogeneous And Heterogeneous Nucleation




Surfaces Lecture 17 Determining Diffusion Coefficients In Practice
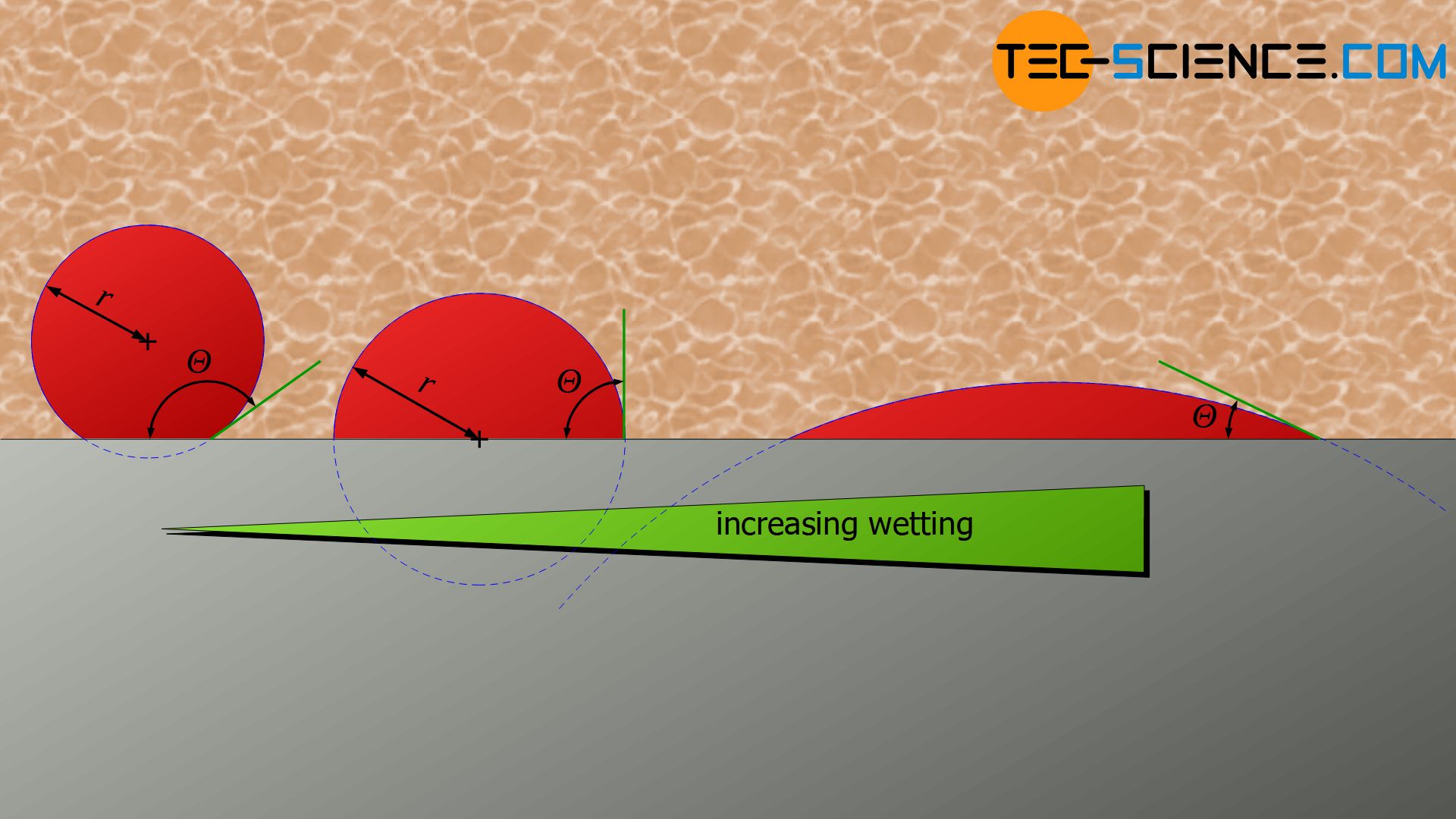



Heterogeneous Nucleation Tec Science
コメント
コメントを投稿